Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Every community develops its own language, and sim racing is no exception. Understanding the terminology helps you follow guides, analyze setups, and communicate effectively with other racers. This glossary defines key terms you’ll encounter, organized by topic.
Sim Racing
A form of virtual motorsport focused on realism in physics, car handling, and competition.
Simulator
A racing title that prioritizes accuracy in car behavior and physics. Examples: iRacing, Assetto Corsa Competizione, rFactor 2.
Simcade
A hybrid between simulation and arcade, balancing realism and accessibility. Examples: Gran Turismo, Forza Motorsport.
Arcade Racer
Games designed for fun and speed rather than realism. Examples: Need for Speed, Burnout.
Force Feedback (FFB)
The resistance and vibrations transmitted through a wheel to simulate tire grip, surface texture, and vehicle weight transfer.
Apex
The innermost point of a corner. Hitting it correctly maximizes speed and stability.
Brake Bias
Distribution of braking force between front and rear wheels. Adjusting bias affects balance and braking stability.
Rotation
How easily a car’s rear end turns through a corner. Rotation results from a mix of steering input, slip angle, and weight transfer. More rotation can help the car point toward corner exit; too much causes oversteer.
Trail Braking
Easing off the brake gradually into a corner to maintain front-end grip and help rotation.
Throttle Modulation
Fine adjustment of throttle to maintain traction and prevent wheelspin during acceleration.
Oversteer
When the rear tires lose grip first, causing the car’s back end to slide outward.
Understeer
When the front tires lose grip first, causing the car to push wide through the turn.
Heel-Toe Downshift
A braking and downshifting technique that matches engine and wheel speed for smoother corner entry.
Slip Angle
The difference between the tire’s steering direction and its actual travel direction. Small slip angles generate grip; large ones cause slides.
Tire Compound
The rubber blend defining grip and wear rate. Softer compounds provide more traction but wear faster.
Aero (Aerodynamics)
Forces generated by wings and bodywork that create downforce, improving grip at speed.
Weight Transfer
The shifting of a car’s mass between tires under braking, acceleration, or cornering. Managing it is key to balance.
Caster / Camber / Toe
Alignment settings affecting handling:
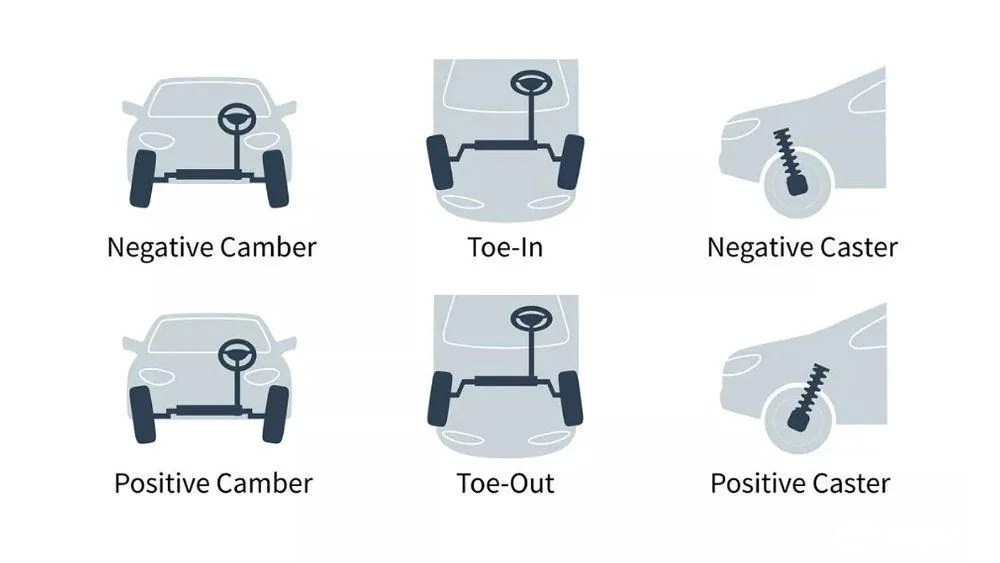
Ride Height
Distance between the car’s chassis and the ground. Lower ride height improves aero but may reduce stability over bumps.
Gear Ratio
Determines acceleration and top speed characteristics. Shorter ratios give faster acceleration but lower top speed.
Wheelbase
The motor unit powering the steering wheel. Can be gear-driven, belt-driven, or direct drive (DD).
Direct Drive (DD)
Wheel directly connected to the motor shaft. Provides precise, high-torque feedback.
Potentiometer Brake
Uses a variable resistor to measure pedal travel. Common in entry-level sets; less consistent over time.
Load Cell Brake
Measures pedal pressure rather than travel distance for accurate braking feel.
Hydraulic Brake
Uses fluid pressure to mimic real-car hydraulic systems. Provides progressive resistance and high realism, typically in premium pedals.
Rig / Cockpit
The frame supporting seat, wheel, pedals, and shifter.
Button Box
A panel with programmable buttons for in-game functions like ignition, headlights, or pit requests.
H-Pattern Shifter
Manual gear shifter using a classic “H” layout.
Sequential Shifter
Push/pull shifter allowing quick up or down shifts in sequence.
Handbrake
Used primarily in rally or drift simulations to initiate slides.
Wheel Rim
Interchangeable steering wheel component. Different rims suit different vehicle types (GT, Formula, Rally).
Quick Release (QR)
Mechanism allowing fast swapping of wheel rims.
Triple Monitors / VR
Display setups. Triple screens provide peripheral vision; VR enhances immersion.
FOV (Field of View)
Camera angle defining how much of the virtual cockpit and track are visible. Correct FOV improves spatial awareness.
Motion System
Hardware that physically moves the rig to simulate g-forces and terrain effects.
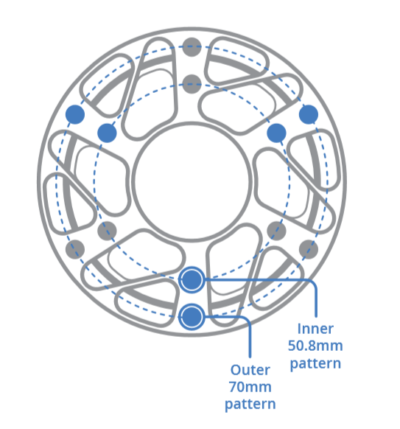
PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter)
The diameter of the imaginary circle that passes through the centers of all bolt holes on a wheel hub or adapter. In sim racing, it’s typically written as both the number of bolts and the circle size (for example, 6×70 mm). The 6×70 pattern—six bolts on a 70 mm circle—is the most common across Fanatec, Simucube, and Ascher wheels. Matching PCD ensures that bolt holes line up between your wheel rim, hub, and quick release.
Telemetry
Real-time data from the sim, such as speed, brake pressure, and tire temperature. Used for performance analysis via tools like VRS or Motec.
Setup
A car’s configuration including suspension, aerodynamics, gearing, and tire pressures.
Ghost Car
A transparent replay of a previous lap used as a visual benchmark for improvement.
Hotlap
A single, all-out lap attempt to set the fastest possible time.
Lap Delta
Real-time time difference between your current and reference laps.
Replay
A recorded session for analysis or content creation.
HUD (Heads-Up Display)
On-screen data showing speed, lap times, and telemetry information.
Grid
The race starting lineup determined by qualifying or reverse-grid rules.
Split
Online races are divided into groups (splits) based on driver skill or rating.
Safety Rating (SR)
Measures driving cleanliness. Incident-free races increase SR.
iRating / Driver Rating
A skill metric that adjusts based on race results and competition level.
Incident Points
Penalties assigned for contact, off-tracks, or spins.
Draft / Slipstream
Reduced air resistance when following another car, allowing higher straight-line speeds.
Blue Flag
Warns that a faster car is lapping you; drivers must yield safely.
Off-Track
Occurs when part of the car leaves the racing surface, potentially invalidating laps.
Pit Strategy
Planning fuel, tire changes, and repairs during a race to minimize time lost and optimize performance.
Endurance Racing
Long-format races (6, 12, or 24 hours) requiring consistency, teamwork, and pit coordination.
League Racing
Structured online championships organized by communities or clubs.
Race Steward / Admin
Official or moderator responsible for enforcing race rules and reviewing incidents.